In the world of finance, business, and everyday communication, abbreviations are often used to simplify lengthy terms. One such abbreviation is “YTD,” which stands for “Year-To-Date.” YTD is commonly used across various sectors to provide a snapshot of performance, progress, or data from the start of the year to the current date. But what does YTD mean in different contexts, and why is it important? This article will dive into the details of YTD meaning, its applications, and how it is calculated.

What Does YTD Mean?
YTD, or Year-To-Date, refers to the period starting from the first day of the current calendar year or fiscal year up to the current date. It provides a simple yet effective way to track performance over time and sees widespread use in financial statements, business reports, and personal finance.
For example, if today is September 27, and the fiscal year started on January 1, the YTD metric would cover the period from January 1 to September 27. This gives a comprehensive look at how a company, individual, or financial portfolio has performed within that time frame.
YTD in Financial Reporting
In financial reporting, YTD meaning is crucial for tracking revenues, expenses, profits, and losses. It helps businesses and investors compare how well a company is performing this year compared to previous periods.
How is YTD Calculated in Finance?
To calculate YTD, you simply add up all the relevant data from the beginning of the year to the current date. For example, if you’re calculating YTD revenue, you would add up all revenue generated from January 1 to the present day.
Formula for YTD calculation:
YTD Metric=∑January 1Current DateRevenue or Expense\text{YTD Metric} = \sum_{\text{January 1}}^{\text{Current Date}} \text{Revenue or Expense}YTD Metric=January 1∑Current DateRevenue or Expense
YTD calculations help companies track their financial health and set future goals. If a business is aiming to hit a certain revenue target by the end of the year, the YTD figure shows them how close or far they are from achieving that goal.
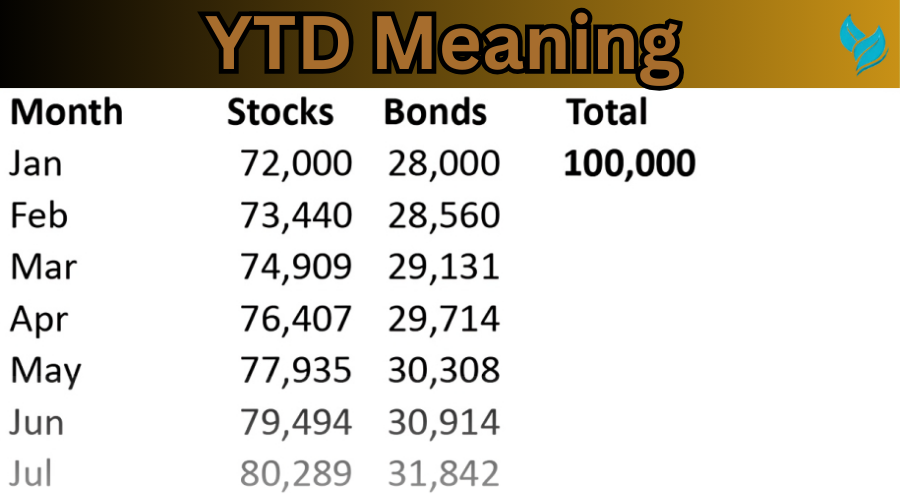
Examples Using YTD Meaning Across Different Financial Aspects Like Stocks and Bonds:
| Period | Example | Stocks | Bonds | Total |
|---|
| YTD (Year-To-Date) | January 1 to Current Date (Example: September) | $10,000 (growth of 5%) | $8,000 (growth of 3%) | $18,000 (total growth of 4%) |
| Previous Year | Last Year’s YTD (Example: September) | $9,500 (growth of 4%) | $7,800 (growth of 2.5%) | $17,300 (total growth of 3.5%) |
| Comparison | Performance Difference | +$500 (1% increase) | +$200 (0.5% increase) | +$700 (total 0.5% increase) |
| Period | Stocks | Bonds | Total |
|---|
Month I (January) and Year to Date (YTD) data for stocks and bonds?
| Month I (January) | $5,000 (growth of 2%) | $3,000 (growth of 1.5%) | $8,000 (total growth of 1.8%) |
| Year to Date (YTD) | $15,000 (growth of 6%) | $12,000 (growth of 4%) | $27,000 (total growth of 5%) |
YTD in Personal Finance
For individuals, the YTD meaning often appears on paycheck stubs, showing the total earnings since the start of the year. This helps employees understand their earnings, tax deductions, and contributions toward benefits like health insurance or retirement plans.
YTD is essential for personal budgeting as it allows individuals to see where their money has gone over the course of the year and whether they are on track to meet their financial goals.
YTD for Personal Budgeting
YTD is also useful for keeping track of personal expenses. By regularly reviewing Year-To-Date spending, individuals can adjust their budget as needed, ensuring that they stay on track throughout the year.
For instance, if you plan to save $5,000 by the end of the year, reviewing your YTD savings allows you to check if you’re meeting your goal or need to adjust your savings plan.
YTD in Stock Market and Investments
In the stock market, YTD meaning plays a significant role in analyzing the performance of investments. Investors frequently use YTD to monitor how well a stock or a portfolio has performed since the beginning of the year. This helps in making informed decisions about buying, holding, or selling investments.
YTD in Portfolio Performance
For investors, YTD is a key metric to track the performance of their portfolio. It provides insights into how much an investment has grown or declined over the course of the year. This figure helps in comparing the portfolio’s performance against benchmarks such as the S&P 500 or other market indices.
By looking at the YTD performance, investors can see if their investments are meeting their expected return rate and adjust their strategy accordingly. For example, if a particular stock has shown substantial YTD growth, an investor may decide to sell and lock in the profits.
Why Is YTD Important?
Understanding YTD meaning is important for several reasons, whether you’re managing a business, handling personal finances, or investing in the stock market. Here are a few reasons why:
- Tracking Progress: YTD allows individuals and companies to track their progress toward annual goals.
- Making Informed Decisions: YTD metrics provide valuable insights, helping businesses and investors make informed decisions based on year-long performance.
- Financial Reporting: YTD figures are commonly used in financial statements to give stakeholders a clear view of a company’s financial health.
- Comparison with Previous Years: YTD figures can be compared with the same period in previous years to gauge growth or decline.
- Personal Finance: For individuals, YTD earnings and expenses help in managing budgets, taxes, and savings plans.
Common Uses of YTD
The YTD meaning is relevant in various real-life situations in multiple ways
- YTD Earnings: Employers often show YTD earnings on paycheck stubs, allowing employees to see how much they have earned over the year.
- YTD Returns: Investors use YTD to measure the returns of their investments from the beginning of the year to the present date.
- YTD Revenue: Companies track YTD revenue to measure how much they have earned since the start of the year.

FAQs
Q1: What Does YTD Stand For?
YTD stands for Year-To-Date, which refers to the period from the start of the current year up to the present day.
Q2: How Is YTD Used in Business?
In business, companies track financial performance using YTD, including revenues, expenses, and profits.
Q3: How Do I Calculate YTD?
To calculate YTD, sum up all relevant data (e.g., revenue, expenses) from January 1 to the current date.
Q4: What Is the Difference Between YTD and MTD?
While YTD covers the period from the beginning of the year to the current date, MTD (Month-To-Date) only covers the current month up to today’s date.
Q5: Is YTD Used in Personal Finance?
Yes, YTD appears in personal finance, often on paycheck stubs, showing the total amount earned since the start of the year.
Conclusion
Understanding the YTD meaning is essential for both individuals and businesses. It offers valuable insights into financial performance, personal progress, and investment returns. Whether you’re a business owner tracking revenue, an employee reviewing your paycheck, or an investor monitoring stock performance, YTD metrics provide a clear snapshot of where you stand relative to your goals. Make sure to regularly review your YTD figures to stay on top of your finances and investments.